Hair loss stages is a term used to describe the progression of hair loss in individuals experiencing various types of hair loss, including male pattern baldness, female pattern baldness, and other conditions. The stages of hair loss can help determine the extent and severity of the condition and guide appropriate treatment options. By understanding the hair loss stages, medical professionals can provide targeted interventions to manage and address the underlying causes of hair loss effectively.
Male pattern baldness, known as androgenetic alopecia, is a common form of hair loss characterized by progressive and symmetrical hair thinning in specific areas of the scalp. It is caused by the combination of genetic and hormonal factors, specifically the influence of androgens on genetically susceptible hair follicles.
This article will delve into male pattern baldness. We will explore the underlying causes of hair loss stages, including the influence of androgens on genetically susceptible hair follicles in this condition. Furthermore, we will discuss various treatment approaches, ranging from medications such as minoxidil and Finasteride to surgical interventions like hair transplantation. Understanding these aspects is vital for individuals seeking effective management strategies for male pattern baldness.
Hair Loss Causes
Male pattern baldness is a complex condition influenced by genetic, hormonal, and environmental factors. Understanding the causes can help individuals proactively manage or prevent hair loss. Let us explore the primary causes of male pattern baldness and shed light on the underlying factors that contribute to this condition.
-
Genetic Predisposition
Genetics is one of the leading causes of male pattern baldness or crown baldness stages. The condition is believed to be inherited through a combination of genes from both parents. If you have a family history of male pattern baldness, there is a higher likelihood that you may develop the condition. The main genetic factor involved is the presence of dihydrotestosterone (DHT), a hormone derived from testosterone.
DHT binds to receptors in the hair follicles, causing them to shrink over time and produce thinner, shorter hairs, eventually leading to baldness.
-
Hormonal Imbalance
Hormonal imbalances can contribute to the development of male pattern baldness. If there is an imbalance in hormone levels, particularly an increase in DHT production, it can accelerate the rate of hair loss. Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) and thyroid disorders can also disrupt hormone levels and lead to hair thinning and baldness.
-
Age
Age is another significant factor contributing to male pattern baldness. Hair loss often starts gradually after puberty and becomes more noticeable with age. As men grow older, the hair follicles become more susceptible to the effects of DHT, leading to progressive hair loss. The exact mechanism of age influencing male pattern baldness is not fully understood. Still, it is believed to be a combination of genetic factors and hormonal changes over time.
-
Poor Scalp Health
The health of the scalp plays a crucial role in maintaining healthy hair. Poor blood circulation, inadequate nutrient supply, and excessive sebum production can negatively impact hair growth. When the scalp is not in optimal condition, it can weaken the hair follicles and contribute to hair loss. Additionally, certain scalp conditions, such as seborrheic dermatitis or scalp psoriasis, can cause inflammation and damage to the hair follicles, leading to hair thinning and baldness.
-
Lifestyle and Environmental Factors
Several lifestyle and environmental factors can contribute to crown baldness stages. Excessive stress levels, smoking, and poor nutrition can all have a detrimental impact on hair health. Stress disrupts the normal hair growth cycle and can lead to increased shedding. Smoking reduces blood flow to the hair follicles, depriving them of essential nutrients. A diet lacking vitamins, minerals, and proteins can weaken hair follicles and accelerate hair loss. Exposure to environmental pollutants and toxins can further exacerbate the condition.
Hair Loss Stages
Understanding the stages of male pattern baldness can help individuals recognize the progression of their hair loss and make informed decisions about treatment options. Let us know more about the stages of male pattern baldness or crown baldness and the characteristic features associated with each stage.
Stage 1: Minimal Hair Loss
A limited amount of hair loss or a receding hairline are the main symptoms of stage 1 male pattern baldness. The hairline may slowly recede at the temples and take on an M shape. The alterations could be slight, but they act as the condition’s first warning indicators. The sensitivity of hair follicles to androgens, especially dihydrotestosterone (DHT), begins to increase. To investigate preventive measures and treatment alternatives that can help slow down hair loss stages and encourage hair regrowth, it is crucial to monitor the evolution of the condition and seek professional counsel.
Stage 2: Mild Hair Loss
As the receding hairline continues, hair loss stage 2 male pattern baldness is characterized by palpable hair loss. The M shape becomes more apparent, and thinning hair on the scalp’s crown region may start to show. Hair loss is more prominent, mainly when damp or styled. It is essential to seek medical guidance to review potential treatment choices and preventive measures. Early management can delay the loss of hair’s progression and improve the likelihood of successful hair restoration.
Stage 3: Moderate Hair Loss
Male pattern baldness stage 3 denotes considerable hair loss. The hair volume on the scalp’s crown area significantly decreases as the hair loss becomes more apparent. A U-shaped pattern of hair develops around the sides and back of the head from the thinning hair on the crown and the receding hairline. As hair thinning becomes more noticeable, people may consider several treatment options to stop additional hair loss and encourage regeneration at this hair loss stage.
It is essential to seek professional help to receive individualized guidance and effective interventions based on the person’s unique needs and objectives. You can consult Dr. Arvind Poswal for the best advice on controlling moderate hair loss issues.
Stage 4: Extensive Hair Loss
Male pattern baldness stage 4 is marked by significant hair loss. At this stage, a larger portion of the scalp is affected by the thinning or complete hair loss. Only a band of hair is left when the U-shaped pattern of hair on the sides and back of the head narrows. The scalp may be more noticeable in the crown area due to substantial hair thinning or complete hair loss, and it is close to crown baldness stage.
People in stage 4 frequently seek more sophisticated treatment options, such as medicines or hair transplantation, to address the considerable hair loss. A hair loss specialist should be consulted to decide the best course of action and discuss each treatment method’s potential advantages and disadvantages.
Stage 5: Advanced Hair Loss
Male pattern baldness stage 5 is the most advanced hair loss stages. The hair left on the sides and back of the head narrows and assumes the shape of a horseshoe. A noticeable scalp results from the significant thinning or complete loss of hair in the crown region. At this point, hair transplantation becomes a more frequent option to explore because it can help restore the hairline and conceal areas of severe hair loss.
However, the amount of hair loss may limit the total coverage that can be achieved with transplanting. People in stage 5 may also consider other choices, such as scalp micropigmentation, a close-cropped hairstyle, or becoming bald. At this time, acceptance and confidence in different haircuts for total baldness are more common.
Stage 6: Severe Hair Loss
Severe hair loss characterizes crown baldness stage 6. At this point, the top of the head’s remaining hair starts to thin out, and the horseshoe pattern on the sides and back of the head continues to fade. Hair follicles in the head region generally endure substantial hair loss and go dormant. Due to the lack of scalp donor hair, hair regrowth becomes difficult, and hair transplantation may have restrictions.
People at stage 6 frequently look into other solutions, such as scalp micropigmentation, which entails tattooing tiny dots to resemble hair follicles. They may even embrace a cleanly shaven head or an utterly bald appearance. Acceptance of one’s looks and gaining confidence in them become essential in this stage.
Stage 7: Complete Baldness
The top of the scalp is entirely bald at stage 7 of male pattern baldness. It is also known as the baldness stage. Around the sides and back of the head, all that is left is a horseshoe-shaped band of hair. Significant hair regrowth is complex since most hair follicles on the top of the head are dormant or inactive. Due to a scarcity of donor hair, hair transplantation may not be possible. Alternative methods, such as scalp micropigmentation or using hair systems, can assist in simulating a precisely shaven or well-groomed appearance.
Accepting baldness becomes a popular decision, and people frequently concentrate on grooming and keeping up a clean-shaven or purposefully bald appearance. Confidence and self-acceptance are crucial to manage stage 7 of male pattern baldness.
Treatment Options For Male Pattern Baldness
Let us explore the various treatment approaches for male pattern baldness, ranging from medications and topical solutions to surgical interventions.
Medications
Some popular medications that can be used in early hair loss stages of male pattern baldness are:
-
Finasteride (Propecia)
Finasteride is an oral medication that inhibits the conversion of testosterone into dihydrotestosterone (DHT), the hormone responsible for shrinking hair follicles in male pattern baldness. By reducing DHT levels, finasteride helps to slow down hair loss and even stimulate regrowth in some cases.
It is most effective in the early hair loss stages and should be taken continuously to maintain the benefits. However, it’s important to note that finasteride may cause side effects such as decreased libido or erectile dysfunction in some individuals.
-
Minoxidil (Rogaine)
Minoxidil is a topical solution that is applied directly to the scalp. It is available over-the-counter and does not require a prescription. Minoxidil increases blood flow to the hair follicles and stimulates hair growth, and prevents further hair loss.
It is most effective when used consistently and may take several months to show noticeable results. Minoxidil is generally well-tolerated, but some individuals may experience scalp irritation or unwanted hair growth in other body areas.
Low-Level Laser Therapy (LLLT)
Low-level, red light, or laser comb therapy is a non-invasive treatment option for male pattern baldness stages. It involves exposing the scalp to low levels of laser light, stimulating hair follicles, and promoting hair growth. LLLT can be performed at home using handheld devices or in specialized clinics.
While the exact mechanism of action is not fully understood, it is believed that LLLT increases blood flow to the scalp and enhances cellular metabolism, improving hair growth. It is a safe and painless treatment option, but results may vary among individuals, and consistent use is necessary to maintain the benefits.
Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP) Therapy
Platelet-rich plasma therapy is a relatively new and promising treatment option for male pattern baldness stages. It involves extracting a sample of the patient’s blood, processing it to concentrate the platelets, and injecting the platelet-rich plasma into the scalp. Platelets contain growth factors that promote tissue repair and stimulate hair growth.
PRP therapy is thought to improve the health of hair follicles, increase hair thickness, and slow down hair loss. Multiple sessions are typically required, and results may vary. PRP therapy is generally safe, with minimal side effects.
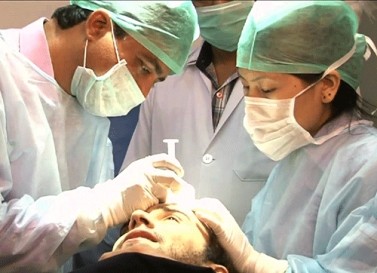
Hair Transplantation
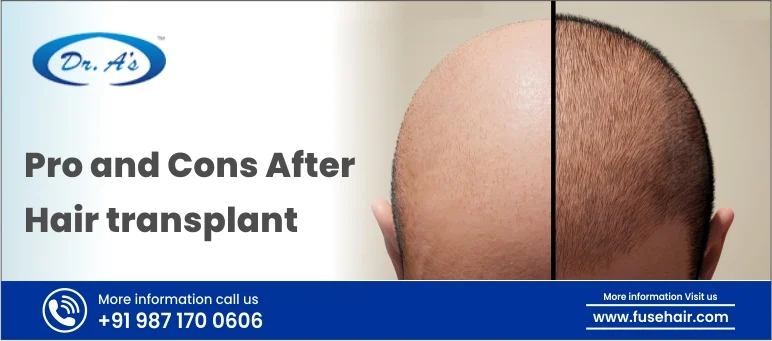
Hair transplantation is a surgical procedure that involves the removal of hair follicles from one part of the body (usually the back or sides of the scalp, where hair is still abundant) and their transplantation to areas of the scalp with thinning or no hair. The transplanted hair follicles continue to grow hair in their new location, creating a more natural appearance. Different techniques include follicular unit transplantation (FUT) and follicular unit extraction (FUE).
Hair transplantation is a highly effective and permanent solution for male pattern baldness stages. However, it is a more invasive and costly option than non-surgical treatments, and the procedure’s success depends on various factors, including the surgeon’s skill and the donor hair’s quality. Visit Dr. A’s Clinic for affordable yet best hair transplantation treatment.
Camouflage Techniques
For individuals who prefer non-invasive approaches or are not suitable candidates for medications or surgical interventions, various camouflage techniques are available to conceal the appearance of thinning hair or bald patches. These include:
-
Hairstyling
Choosing a suitable hairstyle can make a significant difference in disguising hair loss. Opting for shorter hairstyles or those that create volume and texture can help minimize the visibility of thinning areas.
-
Hair Fibers
Hair fibers are microscopic particles that adhere to existing hair strands, instantly adding thickness and coverage. These fibers are available in various colors to match different hair shades and can be applied easily.
-
Scalp Micropigmentation (SMP)
SMP involves the application of pigments to the scalp to mimic the appearance of hair follicles. This technique creates the illusion of a closely cropped hairstyle and can effectively camouflage areas of baldness.
-
Wigs or Hairpieces
Wearing a wig or hairpiece is another option for individuals seeking immediate coverage for extensive hair loss. High-quality wigs or custom hairpieces can provide a natural-looking and comfortable solution.
Conclusion
In conclusion, male pattern baldness is a widespread disorder that develops in stages, beginning with a receding hairline and possibly progressing to substantial hair loss. To deal with this problem, there are various efficient therapy alternatives accessible. People have many options to treat crown baldness stages and regain confidence, including topical or oral drugs, low-level laser therapy, hair transplantation, and scalp micropigmentation. To select the best treatment choice based on hair loss stages and the needs of each patient, consulting with a medical expert or hair loss specialist is essential.
You can consult Dr. Arvind Poswal, who offers efficient hair restoration procedures. He is proficient in hair loss procedures, such as Follicular Unit Hair Transplant, Follicular Unit Separation Extraction, FUE Hair Transplant, Eyebrows Restoration, and Beard Restoration. Following a comprehensive assessment, he tailors his treatments to each patient’s scalp condition and hair loss pattern.
FAQs
-
Is male pattern baldness reversible without treatment?
Male pattern baldness is a progressive condition; without intervention, it is unlikely to reverse on its own. However, with appropriate treatment, it can slow down the progression of hair loss, promote hair growth, and potentially restore some lost hair.
-
Is female pattern baldness as common as male pattern baldness?
Female pattern baldness is less common than males but can still affect many women. While male pattern baldness typically follows a distinct pattern of hair loss, female pattern baldness tends to cause overall hair thinning, particularly on the top of the scalp. It is estimated that about 40% of women experience some degree of hair loss by age 50.
-
How effective are topical and oral medications in treating male pattern baldness?
Topical medications like minoxidil have effectively slowed hair loss, promoted regrowth, and increased hair thickness. Oral medications such as Finasteride have also successfully inhibited the hormone responsible for hair loss in men. However, the effectiveness of these medications may vary from person to person, and it’s essential to consult a healthcare professional for personalized advice.
-
Is hair transplantation a permanent solution for male pattern baldness?
Hair transplantation is often considered a long-lasting solution for male pattern baldness. It involves transplanting hair follicles from donor areas to the balding or thinning areas, resulting in natural-looking hair growth. However, it’s important to note that the procedure’s success depends on several factors, including the individual’s suitability as a candidate and the surgeon’s expertise.
-
Are there non-surgical options for managing male pattern baldness?
Yes, there are non-surgical options available for managing male pattern baldness. Low-level laser therapy (LLLT) is a non-invasive treatment that stimulates hair growth through light therapy. Scalp micropigmentation is another non-surgical option that uses tattooing to create the appearance of a fuller head of hair. These options can suit individuals who prefer non-surgical interventions or have specific needs and preferences.